Tax consulting is a rewarding career and business model. You get to work with firms, businesses, offices, and individuals to show them how to apply any tax law. You are the go-to individual for questions about tax preparation and tax returns. And you are key to the financial success of your clients. On top of that, the field of tax consultation is very lucrative. But how do you become a tax consultant?
It is no wonder that tax law consultancy has become a competitive business. If you are trying to get a college degree in accounting or a similar degree, think about what it involves. Also, if you want to make a career change in this field, you need to be familiar with:
- Career options
- Education requirements
- Experience needed
- Salary projections
- And other requirements
This article will tell you everything about how to become a tax consultant and a successful one!
What is a Tax Consultant?

Tax consultants are there to help individuals and small and large companies with their tax questions. They advise clients on how to handle their tax responsibilities and lower their tax obligations.
In the larger scheme of things, they can advise clients on how to set up a tax strategy and cover their tax liabilities. For the consultant that means studying federal and state tax laws, communicating, and applying them. The goal is to benefit the client and reduce unnecessary tax payments. Other responsibilities could include
- Preparing tax returns
- Payroll taxes
- Compliance with local and national tax laws
It is thus crucial that tax advisors stay up-to-date with the latest state and federal tax requirements. But how can you become a tax consultant? Tax professionals need to have an EA or CPA degree. It is the state's Board of Accountancy that asks for them and determines the requirements for obtaining them. A CPA includes a four-part national exam and an accounting course consisting of 150 college hours.
Important soft skills include good spoken and written communication skills. As a tax advisor, you need to be able to explain concepts that are foreign to your clients.
Where do tax consultants work? Here are some examples:
- Financial consulting firms
- Large companies
- Law offices
- Public accounting firms
Tax Consultants’ Duties and Functions
A tax consultant is more than a tax preparer or a person who signs financial documents. Preparing and filing tax returns is the last part of a consultant's duties. The description above shows that the work of these tax professionals is relevant throughout the fiscal year.
To elaborate on this, the following are some of the functions of a tax consultation professional:
- Investigate the impact of current financial activity on future tax returns
- Have all tax-related issues under control so that submitting tax return documents is a simple and fast process
- Help new businesses to get all their tax obligations sorted, even before starting
- Give clients the confidence that they are fulfilling their legal obligation without paying unnecessary taxes
- Provide tax planning when it comes to acquisitions, mergers, and sales
Important Tax Consultant Skills
We have discussed the most important functions of a tax advisor; besides that, building constructive relationships with clients is crucial.
A tax consultant needs to have a certain social awareness, understand what a client needs, and be able to communicate well. Knowing how to ask the right questions is a skill that many tend to overlook but is essential. Speaking and writing skills allow a consultant to put the knowledge of tax rules into practical use for clients and coworkers.
How do you become a tax consultant desired by many big companies? This involves many other skills. You can read about some of them in the section below.
Mathematical skills
To prepare tax returns you need good mathematical insight. Much of the work of a tax consultation professional involves making calculations. If you want to get into this field, you will need a certain aptitude for calculations, and preparing mathematical projections.
Time and project management
Most tax consultant professionals work with several clients at a time. That means managing many tasks at a time. Excellent project and time management skills are crucial for success.
Attention to detail and accuracy
Part of the work of a tax consultant is reviewing piles of documents. When you have to go through large numbers of documents you need to have a keen eye and the ability to focus on what is important. There could be small inconsistencies, and you need to be able to spot them. The goal is to plan and prepare taxes in the best way possible.
Creativity and competence
The main goal of tax professionals is to ensure compliance and reduce tax liability. They need to consider state, regional, and federal tax laws. At the same time, they serve the interests of their clients. In the end, the client wants to pay as little in taxes as possible, so that requires detailed knowledge of the client's particular situation and a creative approach.
Technical skills
Computers and computer software help in the work of a tax consulting expert. Some create their own customized spreadsheets to make their work faster and easier. A measure of tech-savviness is a prerequisite for successful tax consultants. Records need to be correct, clear, and consultable.
Communication abilities
Most individuals and small business owners have little knowledge of complex financial accounting. They often leave decisions up to their tax professionals. But consultants need to be able to explain their conclusions and suggestions in a way that is understandable to their clients. They are somewhat like teachers. They need to explain concepts related to small business tax preparation checklist and terms that may be unfamiliar to those without a formal education in the matter.
Assertiveness
The client's needs are the priority, but there are times when you cannot give in to their desires. Putting your foot down is also vital when it comes to the matter of receiving payments for your work. Some consultants have had to defend their good name against baseless accusations.
What Formal Education Do You Need to Become a Tax Consultant?
It may surprise you that requirements for tax professionals are rather flexible. There are different careers you can study to get your formal education. You can study accounting, business, or law.
It is not an absolute rule but most professional tax experts have a bachelor's degree in finance or accounting. In addition, many have a bachelor’s degree with a specialized accreditation, CPA credential (Certified Public Accountant).
Some consultants have chosen to specialize in a specific field that requires specialized training or education, like international or corporate tax. These fields of tax law warrant their own tax expertise. Continuing education is necessary to keep up-to-date with the latest changes in tax laws.
Here are some certifications you should get to become a successful tax consultant:
- Enrolled Agent (EA):
An Enrolled Agent is a federally authorized tax practitioner empowered by the U.S. Department of the Treasury. EAs specialize in taxation and have unlimited rights to represent taxpayers before the Internal Revenue Service (IRS). Obtaining EA status demonstrates proficiency in federal tax matters, including tax preparation, representation, and advocacy.
- Certified Public Accountant (CPA):
A CPA designation is widely recognized and respected in the accounting and tax professions. CPAs are licensed by state boards of accountancy and are authorized to offer a broad range of accounting services, including tax consulting. CPA certification signifies mastery of accounting principles, taxation, and ethical standards, making CPAs trusted advisors in tax matters.
- Chartered Tax Advisor (CTA):
The CTA qualification is awarded by professional tax bodies in various countries, such as the Chartered Institute of Taxation (CIOT) in the UK. CTAs are experts in tax law and practice, specializing in providing tax advice and planning services to individuals and businesses. CTA certification demonstrates advanced knowledge of complex tax issues, enabling practitioners to offer specialized tax solutions to clients.
Importance of certifications for becoming a tax consultant
Certification programs rigorously assess candidates' knowledge, skills, and competence in tax matters, ensuring that certified professionals are well-equipped to handle complex tax issues.
Clients and employers often prefer to work with certified tax consultants due to the assurance of their expertise and adherence to professional standards of conduct and ethics.
Holding prestigious certifications opens up opportunities for career advancement, such as higher-paying roles, leadership positions, and consulting opportunities with prestigious firms.
Certain certifications, such as EA, grant practitioners the legal authority to represent clients before tax authorities, enhancing their ability to resolve tax disputes and advocate on behalf of clients effectively.
Technology and Tools in Modern Tax Consulting Practices
From tax preparation to client management, various software tools empower you to effectively manage your tax consulting business. Here are the best tools to make your life easier:
Tax preparation software
Tax consultants rely on advanced tax preparation software to accurately prepare and file tax returns for individuals and businesses. These software solutions automate repetitive tasks, perform complex calculations, and ensure compliance with ever-changing tax laws and regulations. Features such as electronic filing, error checking, and integration with financial software streamline the tax preparation process, saving time and reducing errors.
Adopting tax workflow solutions helps consultants manage their processes more efficiently, from document collection to final filing, ensuring smoother operations and better client service.
Research databases
Tax consultants utilize research databases and online resources to stay updated on the latest tax laws, rulings, and interpretations. Access to comprehensive databases enables consultants to conduct thorough research, analyze relevant tax issues, and provide accurate advice to clients. Real-time updates and alerts ensure consultants are aware of changes that may impact their clients' tax situations, allowing for proactive tax planning and compliance.
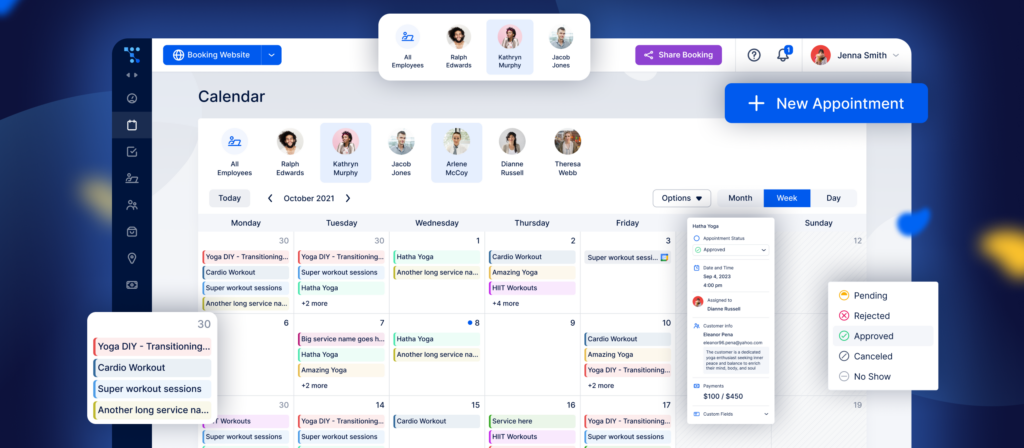
Booking software for tax consultants
As the name suggests, tax consultants often do consulting sessions. If you want to become one, it’s crucial to organize your business the right way from the start.
YOUR success story starts with booking software to streamline your calendar
Trafft is a specialized consulting booking software tailored to the needs of tax consultants. It enables you to manage your schedules, appointments, and client bookings efficiently.
Features such as online booking, appointment reminders, and calendar synchronization streamline the appointment booking process, saving time and reducing administrative burdens.
With Trafft, you can focus more on serving your client's needs and less on managing your schedule, ultimately enhancing productivity and client satisfaction.
What do you get with Trafft?
Beyond basic booking features, Trafft offers a comprehensive suite of features specifically designed to meet the unique scheduling and appointment management needs of tax consultants.
Here are Trafft's most important features that tax consultants can leverage to streamline their operations and enhance client service:
- Trafft supports group bookings, allowing tax consultants to schedule appointments for multiple clients or team members simultaneously. This feature is especially useful for tax workshops, seminars, or group consultations.
- Tax consultants can customize their Trafft booking pages with their branding, logo, and colors to create a professional and consistent client experience.
- Consultants can also add custom fields or questions to the booking form to gather specific information from clients.
- Accept secure online payments from clients at the time of booking or after services are rendered, streamlining the payment process and improving cash flow.
- Integrate Trafft with popular virtual conferencing tools like Zoom, Microsoft Teams, or Google Meet to host virtual client meetings and consultations seamlessly.
- Set your availability preferences, including working hours, break times, and days off, to ensure that clients can only book appointments when you're available.
- Gain valuable insights into your appointment activity and business performance with Trafft's built-in reporting and analytics tools.
But wait until you hear this!
Tax consultants can use Trafft for free to explore its features and see how it can benefit their practice. The free plan has all the features you need and it’s for up to 5 users.
How Long Does It Take to Become a Tax Consultant?
The time it takes to become a tax consultant depends on the kind of training or career. Common steps on the road to becoming one are as follows.
Choosing the industry
There is much you can do to prepare yourself. Try to find as much information as you can. You can read books about tax law and see whether you find it interesting or not. On the internet, you can also find information about what it's like to be a tax consultant. Other sources of information are workshops and webinars.
Earn a bachelor's degree
After you decide to become a tax professional, you need to choose the right major. Most people who work in the field of tax consultancy have a bachelor's degree or an associate degree. If you want to have more responsibility, consider working toward a master's degree.
Get your credentials
As mentioned before, you will also need to earn EA or CPA credentials. A state's Board of Accountancy is the responsible institution for these credentials. CPA involves a four-part national exam and 150 course hours in accounting or a similar field.
EA certificate programs involve an IRS registration. The IRS will have to do a background check, and you need to take a special exam to enroll. If you have previous experience in a tax-related position you may bypass some of the requirements. With that, you will be able to get a Preparer Tax identification number, which is important since you need that number when you prepare tax returns for someone else.
Gain experience
Most employers consider someone with three years of working experience. Keep in mind, though, that quality is more important than the amount of work experience. This is especially true if you want to work at the cutting edge of innovation.
Previous work as an accountant or auditor for a company, NPO, or accounting firm counts as experience. Work for the state revenue department or IRS counts as well. With that kind of experience, you can start working as a tax advisor.
Enroll in continuing education classes
After obtaining a CPA or EA accreditation you need continuing education credits to maintain them.
The exact requirements vary per state. New York, for example, requires a CPA-holder to have 24-40 contact hours per year, depending on the subjects studied. EA holders need to complete 72 education hours every three years.
Land an entry-level job
There are different factors that determine how easy it is to land a job as a tax consultant. It depends on the number of available jobs, personal network, and qualifications. It could take a couple of months to land your first tax consulting job.
Which Specializations Can You Choose as a Tax Consultant?
Tax consulting encompasses a wide range of specialization areas, each requiring unique expertise and skills. Understanding these specialized areas can help aspiring tax consultants identify their interests and tailor their career paths accordingly.
Personal tax planning
Focuses on advising individuals on optimizing their personal finances to minimize tax liabilities.
Includes strategies such as retirement planning, investment optimization, and charitable giving.
Corporate taxation
Involves working with businesses of all sizes to ensure compliance with tax laws and maximize tax efficiency. Tasks may include tax planning for mergers and acquisitions, structuring employee benefits, and managing tax credits and incentives.
International tax
Deals with the complex tax implications of international transactions and operations. Requires knowledge of tax treaties, transfer pricing regulations, and foreign tax credits.
Estate planning
Focuses on helping individuals and families plan for the transfer of wealth to future generations while minimizing estate taxes. Involves drafting wills, establishing trusts, and implementing tax-efficient gifting strategies.
Tax compliance
Involves ensuring that individuals and businesses comply with all relevant tax laws and regulations. Includes preparing and filing tax returns, responding to tax audits, and resolving tax disputes with tax authorities.
Tax controversy and litigation
Deals with representing clients in tax-related disputes and litigation proceedings. Requires strong advocacy skills and knowledge of tax law and court procedures.
State and local tax (SALT)
Focuses on navigating the complexities of state and local tax laws, which vary significantly from federal tax laws. Includes advising clients on sales tax, property tax, and other state and local tax obligations.
Nonprofit taxation
Involves providing tax advice and compliance services to nonprofit organizations.
Requires understanding of tax-exempt status, unrelated business income tax (UBIT), and compliance with IRS regulations for nonprofits.
Specialized industries
Certain industries, such as real estate, healthcare, and technology, have unique tax considerations. Tax consultants may specialize in providing tax services tailored to the needs of clients in these industries.
FAQs About Becoming a Tax Consultant
1. What educational requirements are necessary to become a tax consultant?
Although a specific degree is not necessary to work as a tax consultant, most employers favor applicants who have a background in accounting, finance, or a similar profession. In order to obtain higher roles in the industry, a master's degree in taxation or a similar topic may also be beneficial.
2. What skills are required to become a successful tax consultant?
Excellent analytical and critical thinking abilities, attention to detail, great communication skills, and the capacity to perform well under pressure are characteristics of successful tax consultants. Also, they must be able to use their in-depth understanding of tax laws, rules, and practices in their employment.
3. What are the typical job duties of a tax consultant?
Tax consultants help clients with a variety of tax-related problems, such as tax compliance, tax planning, and tax return preparation. They also offer guidance on the tax ramifications of financial decisions, mergers and acquisitions, and commercial transactions.
4. What is the earning potential for tax consultants?
Tax consultants' earning potential varies greatly depending on criteria like experience, education, region, and type of company. As of May 2020, the median annual wage for tax preparers was $47,520, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics.
5. How do I gain experience in tax consulting?
Working at an accounting firm or tax preparation service is often a prerequisite for gaining experience in tax consulting. College internships and part-time jobs can both help students gain expertise in tax planning and preparation.
6. Is it necessary to obtain a professional certification to become a tax consultant?
A professional qualification, such as that of a Certified Public Accountant (CPA) or Enrolled Agent (EA), can boost one's credibility and lead to more employment options in tax consulting, while it is not necessarily necessary.
7. What kind of clients do tax consultants typically work with?
A wide range of clients, including individuals, small enterprises, corporations, non-profit organizations, and government agencies, may be served by tax consultants. Some people might specialize in serving a certain group of clients or industries.
8. What is the job outlook for tax consultants in the current market?
Tax-related advice and services will continue to be needed by firms and individuals, therefore the career prognosis for tax advisors is usually favorable. For tax preparers and accountants, the Bureau of Labor Statistics projects a 3% increase in employment until 2029.
9. Are there any legal or ethical considerations that I should be aware of as a tax consultant?
Tax consultants must conform to all applicable tax laws and regulations as well as the moral guidelines established by organizations like the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA).
10. How do I market myself and build a client base as a tax consultant?
As a tax consultant, cultivating a clientele base often entails networking, forming connections with other professionals in the field, and creating a strong online presence on social media and business websites. Referrals from pleased customers can also be an effective marketing strategy.
Final Thoughts on How to Become a Tax Consultant
Some important and practical tips were presented in this article.
You have learned that as a tax consultant, you can work for a company or on a freelance basis. The internet has opened up many opportunities for professionals in this field. Through it, you can reach a global audience.
Tax consulting has become a very competitive field though, so you need all the help you can get. You will probably want to invest in management software. Continuing education and earning certifications is a must if you want to be an attractive candidate.
Ready to Dive in for More Fun?
Check out these extra resources to uncover all the details about the consulting business:
- How to Start an Online Consulting Business: The Complete Guide
- The 30 Best Apps for Consultants
- How to Get Clients as a Consultant
- How Much to Charge as a Consultant
- How to Run a Consulting Business & Be Successful
- The Best Consultant Scheduling Software for Busy Consultants
- Consulting Slides Best Practices & Examples from Big Companies